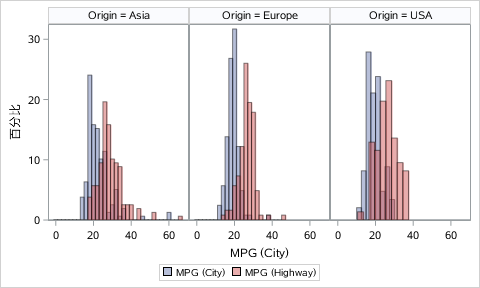
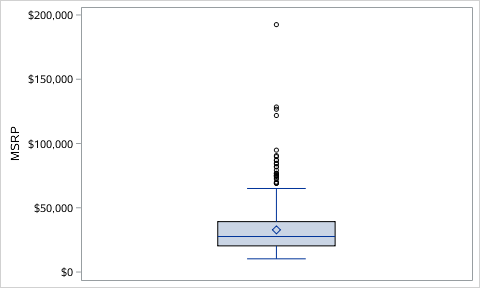
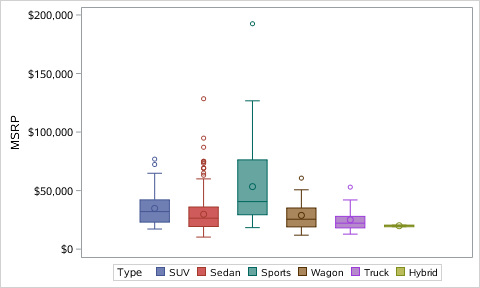
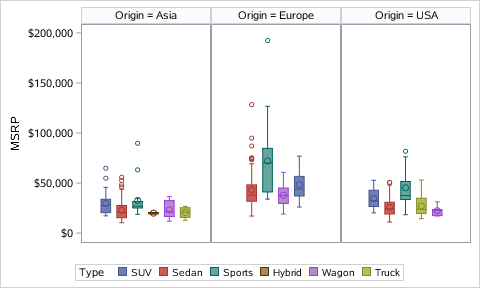
Numpy Basics: Arrays and Vectorized Computation
Magic Methods
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| %quickref | Display the IPython Quick Reference Card |
| %magic | Display detailed documentation for all of the available magic commands |
| %debug | Enter the interactive debugger at the bottom of the last exception traceback |
| %hist | Print command input (and optionally output) history |
| %pdb | Automatically enter debugger after any exception |
| %paste | Execute preformatted Python code from clipboard |
| %cpaste | Open a special prompt for manually pasting Python code to be executed |
| %reset | Delete all variables/names defined in interactive namespace |
| %page OBJECT | Pretty-print the object and display it through a pager |
| %run script.py | Run a Python script inside IPython |
| %prun statement | Execute statement with cProfile and report the profiler output |
| %time statement | Report the execution time of a single statement |
| %timeit statement | Run a statement multiple times to compute an ensemble average execution time; useful for timing code with very short execution time |
| %who, %who_ls, %whos | Display variables defined in interactive namespace, with varying levels of information/ verbosity |
| %xdel variable | Delete a variable and attempt to clear any references to the object in the IPython internals |
Set print options
- Precision
|
|
- Scientific notation
|
|
Array creation Functions
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| array | Convert input data (list, tuple, array, or other sequence type) to an ndarray either by inferring a dtype or explicitly specifying a dtype; copies the input data by default |
| asarray | Convert input to ndarray, but do not copy if the input is already an ndarray |
| arange | Like the built-inrangebut returns an ndarray instead of a list |
| ones, ones_like | Produce an array of all 1s with the given shape and dtype; ones_like takes another array and produces a ones array of the same shape and dtype |
| zeros, zeros_like | Likeonesandones_likebut producing arrays of 0s instead |
| empty, empty_like | Create new arrays by allocating new memory, but do not populate with any values like ones and zeros |
| full, full_like | Produce an array of the given shape and dtype with all values set to the indicated “fill value” full_like takes another array and produces a filled array of the same shape and dtype |
| eye, identity | Create a square N × N identity matrix (1s on the diagonal and 0s elsewhere) |
Why choose np.zeros? It’s the Fastest.
|
|
Indexing and Slicing
An important first distinction from Python’s built-in lists is that array slices are views on the original array. This means that the data is not copied, and any modifications to the view will be reflected in the source array.
If you want a copy of a slice of an ndarray instead of a view, you will need to explicitly copy the array-for example, array_a[2:4].copy().
|
|
Fancy Indexing
Fancy indexing, unlike slicing, always copies the data into a new array.
|
|
Transposing Arrays and Swapping Axes
- Transposing is a special form of reshaping that similarly returns a view on the under‐ lying data without copying anything.
- swapaxes similarly returns a view on the data without making a copy.
|
|
How does NumPy’s transpose() method permute the axes of an array?
|
|
Universal Functions
Ufuncs accept an optional out argument that allows them to operate in-place on arrays:
|
|
Unary ufuncs
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| abs, fabs | Compute the absolute value element-wise for integer, floating-point, or complex values. For non-complex values, fabs is faster |
| sqr | Compute the square root of each element (equivalent to arr ** 0.5) |
| square | Compute the square of each element (equivalent to arr ** 2) |
| Exp | Compute the exponent e^x of each element |
| log, log10, log2, log1p | Natural logarithm (base e), log base 10, log base 2, and log(1 + x), respectively |
| sign | Compute the sign of each element: 1 (positive), 0 (zero), or –1 (negative) |
| ceil | Compute the ceiling of each element (i.e., the smallest integer greater than or equal to that number) |
| floor | Compute the floor of each element (i.e., the largest integer less than or equal to each element) |
| rint | Round elements to the nearest integer, preserving the dtype |
| modf | Return fractional and integral parts of array as a separate array |
| isnan | Return boolean array indicating whether each value is NaN (Not a Number) |
| isfinite, isinf | Return boolean array indicating whether each element is finite (non-inf, non-NaN) or infinite, respectively |
| cos, cosh, sin, sinh, tan, tanh | Regular and hyperbolic trigonometric functions |
| arccos, arccosh, arcsin, arcsinh, arctan, arctanh | Inverse trigonometric functions |
| logical_not | Compute truth value of not x element-wise (equivalent to ~arr) |
Binary universal functions
| Function | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| add | Add corresponding elements in arrays | |
| subtract | Subtract elements in second array from first array | |
| multiply | Multiply array elements | |
| devide, floor_devide | Divide or floor divide (truncating the remainder) | |
| power | Raise elements in first array to powers indicated in second array | |
| maximum, fmax | Element-wise maximum; fmax ignores NaN | |
| minimum, fmin | Element-wise minimum; fmin ignores NaN | |
| mod | Element-wise modulus (remainder of division) | |
| copysign | Copy sign of values in second argument to values in first argument | |
| greater, greater_equal, less, less_equal, equal, not_equal | Perform element-wise comparison, yielding boolean array (equivalent to infix operators >, >=, <, <=, ==, !=) | |
| logical_and, logical_or, logical_xor | Compute element-wise truth value of logical operation (equivalent to infix operators &\ | ,^) |
Basic array statistical methods
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| sum | Sum of all the elements in the array or along an axis; zero-length arrays have sum 0 |
| mean | Arithmetic mean; zero-length arrays have NaN mean |
| std, var | Standard deviation and variance, respectively, with optional degrees of freedom adjustment (default denominator n) |
| min, max | Minimum and maximum |
| argmin, argmax | Indices of minimum and maximum elements, respectively |
| cumsum | Cumulative sum of elements starting from 0 |
| cumprod | Cumulative product of elements starting from 1 |
Array set operations
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| unique(x) | Compute the sorted, unique elements in x |
| intersect1d(x, y) | Compute the sorted, common elements in x and y |
| union1d(x, y) | Compute the sorted union of elements |
| in1d(x, y) | Compute a boolean array indicating whether each element of x is contained in y |
| setdiff1d(x, y) | Set difference, elements in x that are not in y |
| setxor1d(x, y) | Set symmetric differences; elements that are in either of the arrays, but not both |
Linear Algebra
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| diag | Return the diagonal (or off-diagonal) elements of a square matrix as a 1D array, or convert a 1D array into a square matrix with zeros on the off-diagonal |
| dot | Matrix multiplication |
| trace | Compute the sum of the diagonal elements |
| det | Compute the matrix determinant |
| eig | Compute the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a square matrix |
| inv | Compute the inverse of a square matrix |
| pinv | Compute the Moore-Penrose pseudo-inverse of a matrix |
| qr | Compute the QR decomposition |
| svd | Compute the singular value decomposition (SVD) |
| solve | Solve the linear system Ax = b for x, where A is a square matrix |
| lstsq | Compute the least-squares solution to Ax = b |
Pseudorandom Number Generation
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| seed | Seed the random number generator |
| permutation | Return a random permutation of a sequence, or return a permuted range |
| shuffle | Randomly permute a sequence in-place |
| rand | Draw samples from a uniform distribution |
| randint | Draw random integers from a given low-to-high range |
| randn | Draw samples from a normal distribution with mean 0 and standard deviation 1 |
| binomial | Draw samples from a binomial distribution |
| normal | Draw samples from a normal (Gaussian) distribution |
| beta | Draw samples from a beta distribution |
| chisquare | Draw samples from a chi-square distribution |
| gamma | Draw samples from a gamma distribution |
| uniform | Draw samples from a uniform [0, 1) distribution |